# d3-spring-model
This module implements three force-directed layout algorithms to visualize high-dimensional data in 2D space.
1. Basic spring model algorithm. In this model, every data point (node) pairs are connected with a spring that pushes or pulls, depending on the difference between 2D and high-dimensional distance. This is a tweaked version of [D3's force link](https://github.com/d3/d3-force#forceLink) with functionalities removed to improve performance and lower the memory usage.
1. Neighbour and Sampling algorithm. It uses stochastic sampling to find the best neighbours for high-dimensional data and creates the layout in 2 dimensions.
1. Hybrid layout algorithm. It performs Neighbour and Sampling algorithm on a subset of data before interpolating the rest onto the 2D space. Neighbour and Sampling algorithm may also be run over the full dataset at the end to refine placement.
During the interpolation, each node have to find a parent, a closest node that has already been plotted on the 2D space. Two methods of of finding the parents have been implemented.
1. Bruteforce searching. This method takes more time but guaranteed that the parent found is the best one.
1. Pivot-based searching. This method introduce a one-off pre-processing time but will make parent finding of each node faster. The parent found may not be the best one but should still be near enough to provide good results.
These algorithms are useful for producing visualizations that show relationships between the data. For instance:
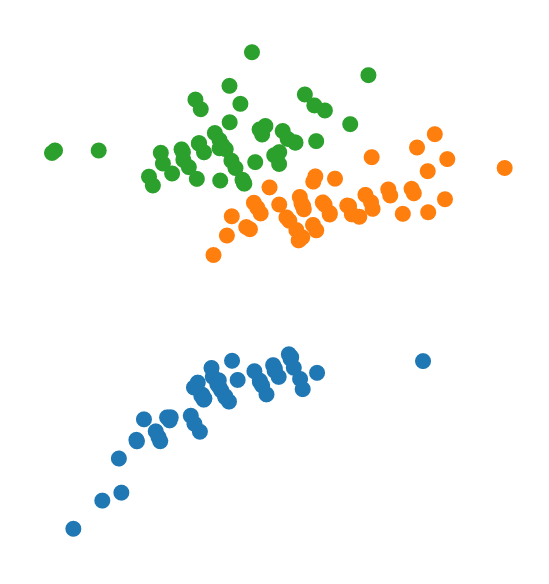
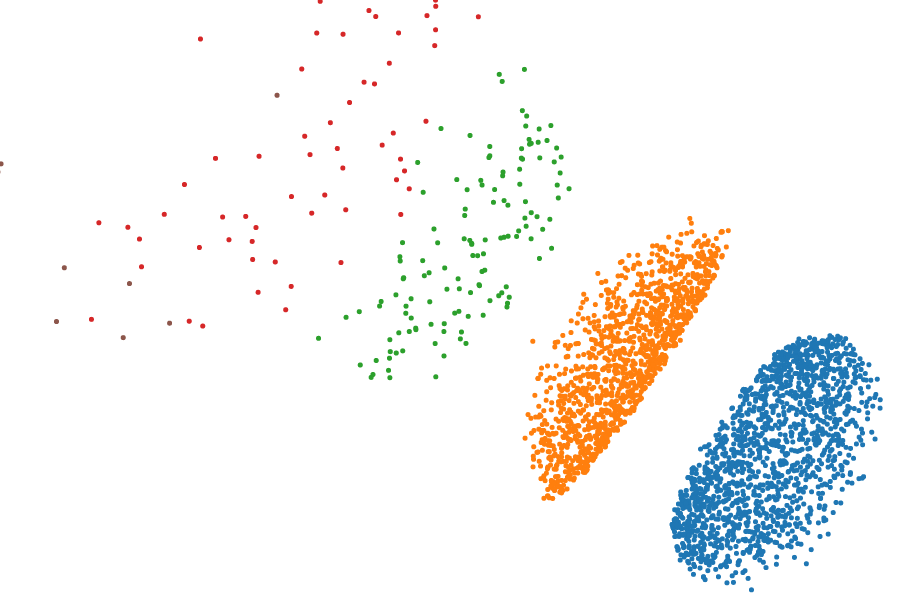
### Authors
Pitchaya Boonsarngsuk
Based on [d3-neighbour-sampling](https://github.com/sReeper/d3-neighbour-sampling) by Remigijus Bartasius and Matthew Chalmers under MIT license.
Based on [d3-force](https://github.com/d3/d3-force) by Mike Bostock under BSD 3-Clause license.
### Reference
- Chalmers, M. ["A linear iteration time layout algorithm for visualising high-dimensional data."](http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=245035) Proceedings of the 7th conference on Visualization'96. IEEE Computer Society Press, 1996.
- Morrison, A., Ross, G. & Chalmers, M. ["A Hybrid Layout Algorithm for Sub-Quadratic Multidimensional Scaling."](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=857191.857738) INFOVIS '02 Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Information Visualization, 2002
- Morrison, A. & Chalmers, M. ["Improving hybrid MDS with pivot-based searching."](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1947387) INFOVIS'03 Proceedings of the Ninth annual IEEE conference on Information visualization, 2003
## Usage
Download the [latest release](https://git.win32exe.tech/brian/d3-spring-model/releases) and load either the full and minified version alongside [D3 4.0](https://github.com/d3/d3).
```html
```
## File structure
- [index.js](index.js) Export list of the module
- [src/](src) Source code of the module
- [package.json](package.json) Node.js moudle descriptor with build scripts
- [img](img) Images for this readme file
- [examples](examples) An example page running all the algorithms implemented
## Building
```bash
npm run build # Clean build folder and build the module into a single js file.
npm run minify # Minify the built js file.
npm run zip # Zip built files and documents for release.
```
See [package.json](package.json) for more details.
## API Reference
### Spring Model
The model connect every nodes together with a "spring", a link force that pushes linked nodes together or apart according to the desired distance. The strength of the "spring" force is proportional to the difference between the linked nodes’ distance and the target distance.
The implementation is based on [d3.forceLink()](https://github.com/d3/d3-force#forceLink) with the list of springs locked down so that every nodes are connected to each other. This comes with the benefit of huge memory usage decrease and lower the initialization time.
# d3.**forceLinkFullyConnected**() [<>](src/link.js "Source")
Creates a new link force with default parameters.
# *springLink*.**distance**([distance])
If *distance* is specified, sets the distance accessor to the specified number or function, re-evaluates the distance accessor for each link, and returns this force. If *distance* is not specified, returns the current distance accessor, which defaults to:
```js
function distance() {
return 30;
}
```
The distance accessor is invoked for each pair of node, being passed the two nodes as two arguments as follow:
```js
function distance(nodeA, nodeB) { return NumberDistanceBetweenAandB; }
```
The resulting number is then stored internally, such that the distance of each link is only recomputed when the force is initialized or when this method is called with a new *distance*, and not on every application of the force.
# *springLink*.**iterations**([*iterations*])
If *iterations* is specified, sets the number of iterations per application to the specified number and returns this force. If *iterations* is not specified, returns the current iteration count which defaults to 1. Increasing the number of iterations greatly increases the rigidity of the constraint, but also increases the runtime cost to evaluate the force.
### Neighbour and Sampling - TO REWRITE
The Neighbour and Sampling algorithm tries to group the nodes based on the distance between them. If the nodes have a low distance, then the force attracts them to each other. If the nodes have a high distance, then the repulsive force pushes them further apart from each other.
In order for it to work properly, a distance function should be specified.
# d3.**forceNeighbourSampling**() [<>](src/neighbourSampling.js "Source")
Initializes the Neighbour and Sampling algorithm with default parameters.
# *neighbourSampling*.**id**([*id*])
If *id* is specified, sets the node id accessor to the specified function and returns this force. If *id* is not specified, returns the current node id accessor, which defaults to the numeric *node*.index:
```js
function id(d) {
return d.index;
}
```
The id accessor is invoked for each node whenever the force is initialized, as when the nodes change, being passed the node and its zero-based index.
# *neighbourSampling*.**distance**([*distance*]) [<>](https://github.com/sReeper/d3-neighbour-sampling/blob/master/src/neighbourSampling.js#L230 "Source")
If *distance* is specified, sets the distance accessor to the specified number or function, re-evaluates the distance accessor for each link, and returns this force. If *distance* is not specified, returns the current distance accessor, which defaults to:
```js
function distance() {
return 300;
}
```
# *neighbourSampling*.**neighbourSize**([*neighbourSize*]) [<>](src/neighbourSampling.js#L222 "Source")
If *neighbourSize* is specified, sets the neighbour set size to the specified number and returns this force. If *neighbourSize* is not specified, returns the current value, which defaults to 6.
# *neighbourSampling*.**sampleSize**([*sampleSize*]) [<>](https://github.com/sReeper/d3-neighbour-sampling/blob/master/src/neighbourSampling.js#L226 "Source")
If *sampleSize* is specified, sets the sample set size to the specified number and returns this force. If *sampleSize* is not specified, returns the current value, which defaults to 3.
# *neighbourSampling*.**stress**() [<>](https://github.com/sReeper/d3-neighbour-sampling/blob/master/src/neighbourSampling.js#L234 "Source")
Returns the stress of the layout.
# *neighbourSampling*.**velocity**() [<>](https://github.com/sReeper/d3-neighbour-sampling/blob/master/src/neighbourSampling.js#L238 "Source")
Returns the average velocity of the iteration.
### Hybrid Layout
### Miscellaneous
# d3.**calculateStress**(*nodes*, *distance*) [<>](src/stress.js "Source")
Calculate stress of a whole system, based on sum-of-squared errors of inter-object distances. *nodes* is the array of all nodes in the system and *distance* is the function to calculate the desired distance between two node objects. *distance* is expected to have the same prototype as the one in [springLink](#springLink_distance).